HOW TO USE THE BIICF
BIICF outlines the competencies both technical and soft skills that are essential to effective performance in the ICT roles. The framework can be used as the basis of ICT talent management processes and provides a common reference for the ICT professionals in performing their daily tasks, and identifying specific competencies needed to perform the tasks or role. This will help to strengthen the capability of the organisation.
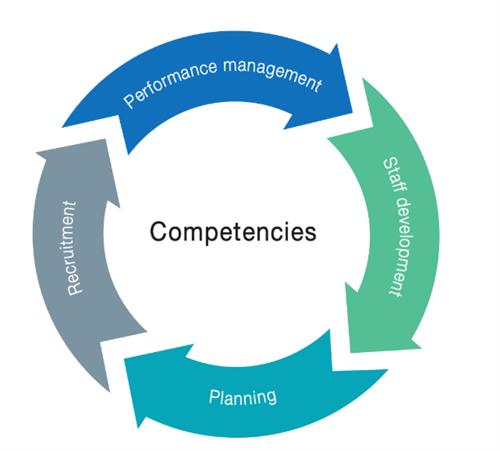
BIICF defines the range of skills and competencies that the ICT professionals needs to have to perform their tasks effectively. It is a guide to assess the knowledge and skills needed for current and future ICT roles as well as the competencies that ICT professionals need to enhance their careers and to create and preserve value for their organisation. Ultimately as depicted in the diagram, the competency framework is essential for holistic workforce management.
STRUCTIRE AND COMPONENTS OF THE BIICF
BIICF consists of the following components for each Job Role:
| Component of the BIICF | Description | |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Job Title |
Name of the Job Role |
|
2 |
Alternate Job Title |
Alternative or other names for similar Job Role |
|
3 |
Sub-Sector |
Name of the common Sub-Sector of the Job Role |
|
4 |
Functional Group |
Name of the main of the Job areas or functions |
|
5 |
Job Family |
Name of the specific Job roles within the Function |
|
6 |
Job Level |
Common Job Level in the company or organisation |
|
7 |
Job Description |
Common list of key duties and responsibilities for the Job Role |
|
8 |
Critical Work Function |
Common job activities or task performed by the Job Holders |
|
9 |
Entry Requirements |
Minimum educational qualification based on Brunei Darussalam Qualifications Framework (BDQF) required to hold this position |
|
10 |
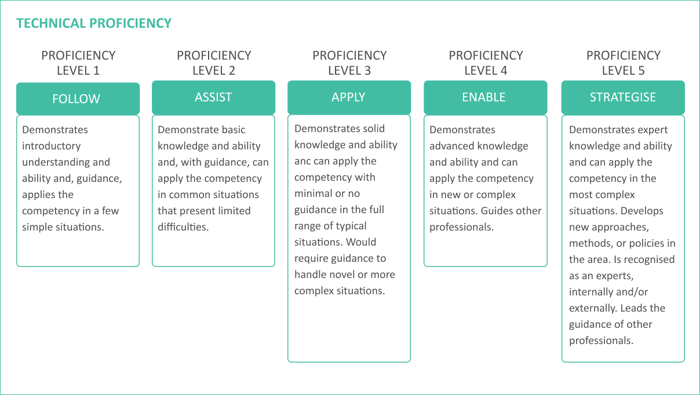
Technical Skills and Competencies |
List of required technical skills and competencies and expected proficiency levels |
|
11 |
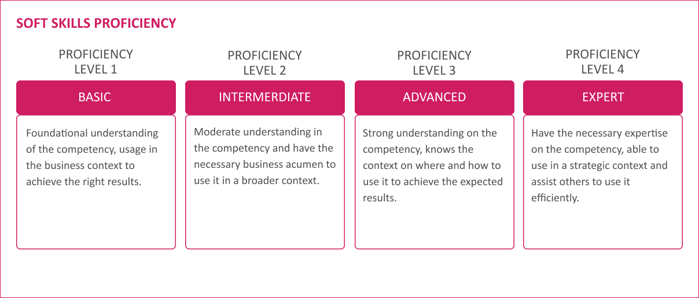
Soft Skills and Competencies |
List of required soft skills and competencies and expected proficiency levels |
|
12 |
Trainings / Professional Certifications |
List of recommended training and professional certifications for the Job Role |
|
13 |
Technical Competency Descriptors |
Description of each technical competency and proficiency level |
|
14 |
Soft Skills Descriptors |
Description of each soft skill and proficiency level |
The list of competencies and recommended trainings provided in this framework is however non-exhaustive and shall be continuously updated so they remain relevant.
This section helps the reader understand how to navigate the BIICF.
The framework is divided into several sections:
- Job Roles – Showing the details of the individual Job Roles. This section contains information such as job description, entry level for the role and its critical work functions. Included in this section is a list of recommended Technical Competencies and Soft Skills that are deemed relevant as well as the Proficiency Level that a person should strive to attain in the role. At the end, a list of recommended Trainings or Certifications is included.
Entry requirements based on BDQF Levels:
| BDQF Levels | Schools Sector Qualifications | Technical and Vocational Education Sector Qualifications | Higher Education Sector Qualifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | Doctoral Degree | ||
| 7 |
|
||
| 6 | Bachelor's Degree | ||
| 5 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
|
|
|
| 1 | BTEC Level Introductory Certificate | Skills Certificate 1 (SQ1) |
APPLICATION OF THE BIICF
This guide has been produced to explain how to use the ICT Competency Framework to get the most out of the framework’s functionality to practically implement competency improvement efforts. The BIICF can be used to meet the businesses needs for:
- Talent attraction and recruitment
- Managing employee performance
- Planning and executing reskilling and upskilling of the workforce
- Transforming the ICT function to fit on the current requirement by the business
As for academia, BIICF will support the following:
- Review of existing curriculum to align with the competencies needed by the industry
- Used as a reference to enhance the curriculum by offering industry specific skills training as top up skills for their undergraduates. This will enhance their graduate employability ratio
- Offer industry relevant skills training to the public which can be an additional revenue generating programme by the academic institutions.
- Introduction of new courses and programmes which is aligned with the current needs of the industry.
Training Providers will benefit from the skills training requirements that have been captured in the BIICF. They can deliver or develop programs by associating themselves to the certification domain partners recommended in the document. At the same time, they can review the programmes they are currently offering and identify to align with those that are sought after by the industry. This is also an avenue for them to make investments to upgrade their training courses and offer new ones which will assist in growth of their business and long-term sustainability.
BIICF helps ICT organisations and the ICT support functions to equip their employees with skills and competencies needed for success. It is designed to help ICT professionals and their employers understand the knowledge required and to assess the skills needed for professionals in existing and desired ICT roles. The need for objectivity, integrity and ethical behaviour underpins the framework, which also supports a commitment to the continuous acquisition of new skills and knowledge.
The reader can use the BIICF flexibly, depending on their organisation’s specific needs. It can be adopted in totality or customised in accordance to the needs of the respective organisations or stakeholders. For organisation which may already have some form of competency framework, they may use the BIICF as a comparison for improvisation where appropriate.
The following sections depict on how the BIICF can be used by the respective stakeholders especially the industry in managing their ICT talent acquisition as well as managing their career cycle. It has been broken into specific activities as had been highlighted earlier.
| Activity | Description | Benefit & Outcome |
|---|---|---|
|
Talent Acquisition |
Recruiting ICT professionals and providing the organisation with relevant data about talent capability availability |
Strengthening overall recruitment practices for the ICT function by:
|
|
Performance Management |
Assessing employees’ performance against predefined goals and behaviours
|
Strengthening the overall effectiveness of performance management and the efficiency of the ICT function by:
|
|
Learning and Development |
Building those capabilities, skills and competencies that the ICT workforce needs to ensure and maintain organisational success
|
Strengthening organisational resilience through a skilled workforce within the ICT function by:
|
|
ICT Function Transformation |
Evolving from a basic support function to transformation enabling function
|
ICT team that helps managers achieve and sustain superior organisational performance by:
|
